CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
GCG serves as the foundation for BRIDS in providing quality services to foster a conducive business climate.
The quality services provided by BRI Danareksa Sekuritas (BRIDS) are the result of corporate governance that is long-term-oriented. GCG serves as a foundation for our business activities to push for company growth and generate added value for all partners and clients in the long run. GCG implementation is based on POJK No. 57/POJK.04/2017 on Implementation of Governance for Securities Companies Conducting Business Activities as Securities Underwriters and Brokers.

Through consistent GCG implementation, BRIDS strives to contribute to the national economy by fostering a conducive business climate through the services provided. Such success in turn will push the growth of BRIDS as a trusted securities company.
WHISTLEBLOWING SYSTEM
Whistleblowing system serves as a medium for all stakeholders to contribute to ensuring integrity and compliance in the business activities of BRIDS.
The input from and participation of all stakeholders are needed to ensure consistent GCG implementation and the conduct of business that is grounded in integrity and compliance. To that end, we provide a medium for reporting of any indication of violation. Through the whistleblowing system, anyone can report a violation to be followed up. We are committed to protecting the confidentiality and safety of the whistleblower.
Brief History of The Company
BRI Danareksa Sekuritas (BRIDS) was established on July 1, 1992, under the name PT Danareksa Sekuritas with the goal to establish and develop Indonesia’s capital market. Providing a one-stop financial solution, BRIDS has handled various capital market transactions as an underwriter, broker and financial advisor for individual, institutional, foreign and domestic, private and government clients. BRIDS has obtained permits as an arranger for Medium Term Note (MTN), Negotiable Certificate of Deposit (NCD), Syndicated Loan, Global Bond, and as Financial Advisor. With the support of 9 branch offices, 36 investment galleries and 3 partners across Indonesia, BRIDS is committed to becoming the best agent for economic growth in Indonesia.
BRI Danareksa Sekuritas Organization Structure

The Board Manual of The Board of Commissioner and Directors
Board Manual of the Board of Commissioner
The Board of Commissioners has the Board Manual in carrying out its duties and responsibilities. The Board Manual for the Board of Commissioners was established on February 1st, 2023, through the Board of Commissioners Decree No. SK.001/BOC/02/2023.
The Board Manual of The Board of Commissioners contains the following:
- Introduction; Background, Vision and Mission, Purpose, and Legal Foundation
- Organization of the Board of Commissioners; Membership of the Board of Commissioners, Appointment, and Dismissal
- Duties, Obligations and Authorities; Description of the Duties of the Board of Commissioners, Obligations of the Board of Commissioners, Authorities of the Board of Commissioners
- Meeting Implementation; Board of Commissioners Meetings, Reporting, and Accountability of the Board of Commissioners
Board of Directors Guidelines
The Board of Directors follows a Board Manual as a reference in carrying out its duties and responsibilities. The Board Manual was established through the Board of Directors' Decree No. KD-05/BRIDS/03/2025, dated March 12, 2025.
The Board Manual includes, but is not limited to, the following:
- Definitions
- Provisions on the Position of the Board of Directors
- Duties, Authorities, and Obligations of the Board of Directors
- Procedures for Board of Directors Meetings
- Conflict of Interest
- Company Introduction Program, Work Ethics, and Working Hours of the Board of Directors
- Leave Provisions and Acting Directors
- Final Provisions
Charter of the Audit Committee and Risk Management Oversight Committee
The Audit Committee and Risk Management Oversight Committee have a Charter that serves as a guideline in carrying out their duties and responsibilities. The Charter of the Audit Committee and Risk Management Oversight Committee was established on October 29, 2025, through the Letter of Charter Renewal of the Audit Committee and Risk Management Oversight Committee of the Board of Commissioners No. SB.008/BOC/10/2025.
The Charter of the Audit Committee and Risk Management Oversight Committee includes, among others:
-
Introduction (Background, General Definition, Legal Basis, Vision and Mission, Purpose and Objective)
-
Establishment and Organization of the Audit Committee and Risk Management Oversight Committee
-
Duties, Responsibilities, and Authorities of the Audit Committee and Risk Management Oversight Committee
-
Procedures and Processes for Meetings and Reporting of the Audit Committee and Risk Management Oversight Committee
-
Budget of the Audit Committee and Risk Management Oversight Committee
-
Closing Provisions
Code of Conduct
BRIDS is committed to conduct the Company's activities by implementing the Company's values, namely AKHLAK (Trustworthy, Competent, Harmonious, Loyal, Adaptive, and Collaborative), and upholding ethical business practices. To support this commitment, the Company had established a Code of Conduct that contained ethical standards in behavior and business. This code had been signed by all the Board of Directors and Board of Commissioners of the Company on May 13th, 2022. This Code of Conduct applied to all Company Personnel at all levels of the organization, from the Board of Commissioners, Board of Directors, and employees of the Company.
Vision, Mission and Work Culture as Foundation of the Code of Conduct
In developing the Code of Conduct, the Company referred to the Vision, Mission, and Work Culture, which serves as guidelines, directions, and objectives in the sustainable development of the Company. As part of the effort to build a conducive work environment and productive work ethics, the Company continued to undertake several initiatives to establish a positive work culture. The Company's work culture contained values, norms, and habits that influenced the thinking, behavior, and way of working of employees and management, leading to an improvement in the quality of the Company's performance.
Principles of the Code of Conduct
The Company's code of conduct contains the main points, including:
- Introduction
- Responsibility
- Diversity and Fair Employment Opportunities
- Working Relationships Among Company Personnel
- Communication Procedure
- Confidential Company Information
- Corporate Identity
- Recording, Documentation, and Bookkeeping
- Safety and Comfort of Work Environment
- Conflict of Interests
- Compliance with the Law
- Equity Trading by Company Personnel
- Compliance with the Code of Conduct
- Internalization, Implementation, Sanctions, and Rehabilitation.
Socialization of Code of Conduct
The Company strives to ensure that the Company's Code of Conduct is communicated and disseminated to all Company personnel, either directly or online
Enforcement and Sanctions for Violation of Code of Conduct
Company Personnel at any level, if proven to have violated the Company's code of conduct, will be subject to sanctions in accordance with the regulations outlined in the Company's Internal Regulations and relevant laws. Additionally, sanctions can also be imposed on:
- Parties who approve actions taken by Company’s personnel;
- Parties who intentionally fail to report, conceal information, or destroy evidence with the intent of covering up violations committed by Company’s personnel;
- Superiors who are aware of violations committed by Company’s personnel under their supervision but fail to report them promptly, resulting in losses to the Company, both financial and non-financial.
Number of Code of Conduct Violations and Sanctions Imposed
Throughout 2023, BRIDS did not record any breaches of the code of conduct, and therefore, no sanctions were imposed.
Risk Management Function and Policy
The Risk Management Committee was formed in accordance with Directors' Decree No: KD-004/BRIDS/02/2024 dated 27 February 2024. The Risk Management Committee is tasked with assisting the Directors in providing information about the risks faced by the Company through risk profile reports so that the Directors can determine possible risk mitigation. applied.
Organization Structure
Chairman: President Director
Member:
- Board of Directors
- Risk Management Division Head
Secretary: Risk Management Division
Duties and Responsibilities
- Determine and approve Policies and Procedures along with transaction approval documents.
- Periodically make changes and updates to the applicable Risk Management Guidelines to ensure:
Reliability of risk assessment methodology; - Adequacy of management information system implementation; And
- Determination of policies, procedures and determination of risk limits.
- Carrying out risk management activities.
- Make decisions and recommendations related to risk management which must be obeyed and implemented by all work units at PT BRI Danareksa Sekuritas.
- Determine authorized officials (approving officers) to approve risk-taking for each business activity and transaction.
- Make decisions or recommendations on a proposed transaction or activity while still guided by internal and external regulations.
- Ensure that provided facilities to customers do not cause conflict with ongoing contracts or mandates obtained by the Company.
Review of the Effectiveness of the Risk Management System
The effectiveness of the Risk Management System is assessed by the Board of Directors and the Risk Management Division regularly. The Company continuously compiles, assesses, and evaluates the risk management system to adapt to external conditions, regulatory developments, and other matters related to the Company's business.
The risk management system within the Company is implemented through the Three Lines of Defense system, involving the separation of business and operational functions, risk management and compliance functions, and audit function. Additionally, the risk management function evaluates the quality of risk management. The assessment for each risk control is categorized into 5 ratings, ranging from rating 1 (strong) to rating 5 (Unsatisfactory). In 2023, the results of the Company's risk profile assessment were ranked 2 "low to moderate." The composite inherent risk was rated low to moderate, and the composite quality of the Company's risk management implementation was rated Satisfactory
Internal Audit and Compliance Functions and Policies
Corporate Secretary
The Corporate Secretary, as a supporting organ for the Board of Directors in implementing corporate governance, plays a crucial role in ensuring the Company's transparency aspect by providing stakeholders with sufficient, accurate, and relevant information. The Corporate Secretary also facilitates an efficient communication program between the Company and its stakeholders to maintain the Company's positive reputation.
Organizational Structure of Corporate Secretary Division
The Corporate Secretary is positioned directly under the Board of Directors and reports directly to the President Director. The Corporate Secretary supervises several functional Units, as outlined in Board of Directors Decree No. KD.015/BRIDS/06/23, dated on June 27th, 2023.
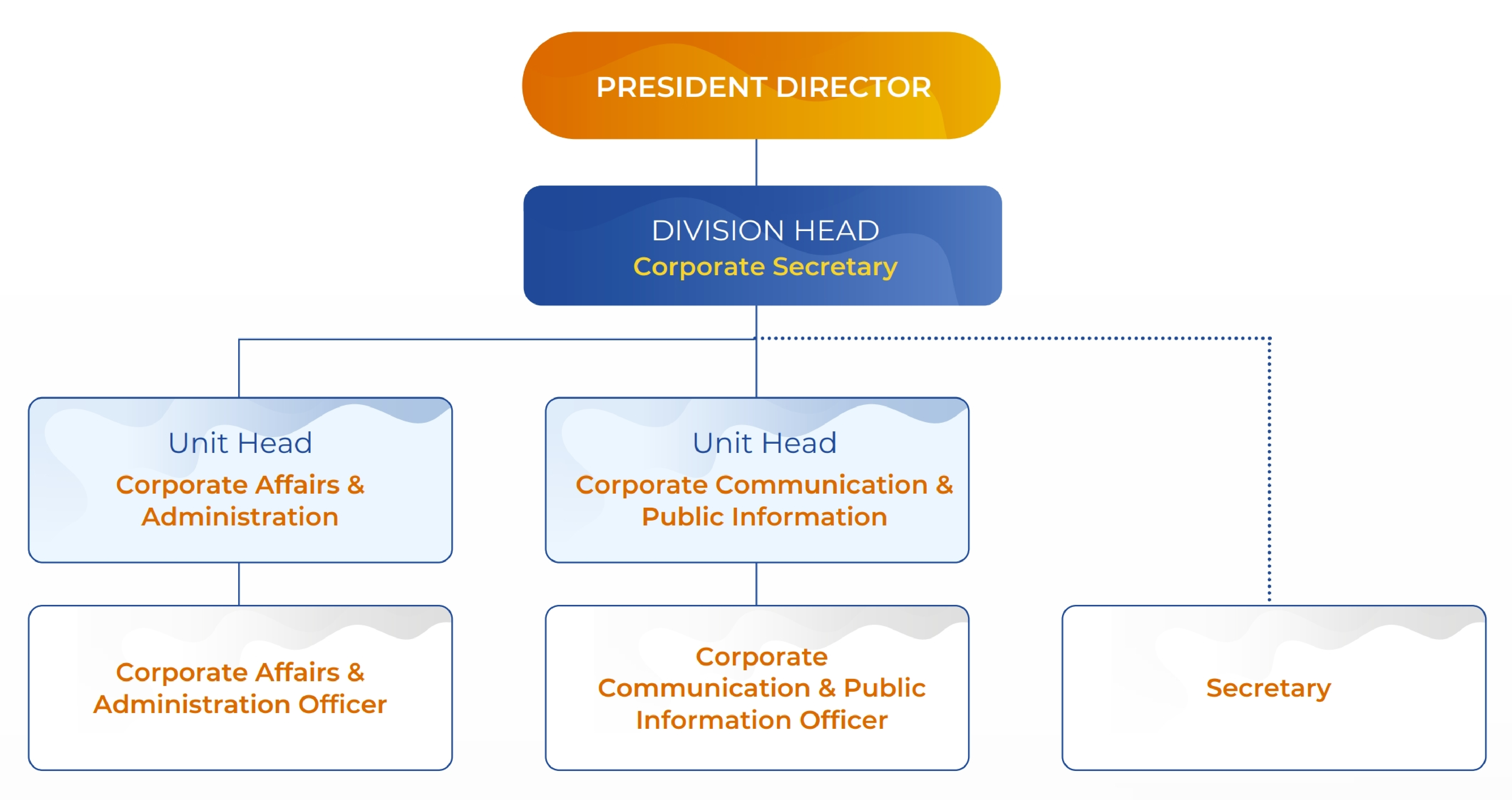
Duties and Responsibilities of Corporate Secretary
The Corporate Secretary has duties and responsibilities, including:
- Providing input to management regarding the use of the Company's visual identity, particularly in marketing tools;
- Controlling the Company's brand image for published materials in alignment with corporate identity and corporate design guidelines;
- Developing marketing plans for Company products, including coordinating activities/events, collaborating with relevant parties, and composing themes, concepts, designs, materials, and promotional guidelines as well as branding;
- Managing the Company's communication with external parties to ensure timely and appropriate conveyance, as well as to anticipate the occurrence of any reputational risk issues affecting the Company;
- Monitoring news about BRIDS across print and online media, and conducting media coverage activities such as articles, press releases, or similar functions;
- Coordinating the preparation of the Annual Report, Company Profile, Calendar, and Religious Greeting Cards;
- Regularly updating information for publication on the Company's website and other social media platforms;
- Handling external communications to foster positive relations with the media, including providing periodic information to authorities, regulators, and other third parties regarding corporate governance performance (in collaboration with the Governance Monitoring function);
- Fulfilling the duty to submit the Company's activities and material reports to FSA and other relevant agencies while ensuring timely submission;
- Preparing Board of Directors Decree, Circular Letters, Power of Attorney, and other legal documents issued by the Board of Directors or jointly with the Board of Commissioners;
- Administering and archiving the Company's documents, including but not limited to the Shareholders Register, Special Register of Board of Directors and Board of Commissioners, Minutes of General Meetings of Shareholders, Minutes of Board of Commissioners and Board of Directors Meetings in compliance with the Limited Liability Company Law and the Company's Articles of Association.
Implementation of Corporate Secretary Duties
Throughout 2023, the Corporate Secretary fulfilled its duties and responsibilities, which included:
- Organized the Annual General Meeting of Shareholders (AGMS);
- Conducted induction programs for newly appointed Board of Directors and/or Board of Commissioners;
- Attended all Board of Commissioners Meetings and Board of Directors Meetings, and managed administrative tasks for the minutes of these meetings;
- Managed public information disclosure, including to the Financial Services Authority and other relevant Regulators, and ensuring availability on the Company's website;
- Ensured the preparation and submission of the Annual Report to Shareholders and relevant regulatory authorities;
- Conducted Social and Environmental Responsibility (CSR) activities.
Internal Audit Division
The Internal Audit Division serves as an independent corporate governance control tool, aimed at assisting the Company and its internal units in achieving their objectives. Through internal audit activities, it provides independent assessments, recommendations, and advice on internal control and risk management within each work unit
Internal Audit Structure and Position
The Internal Audit Division is positioned as a functional unit working directly under the oversight of the President Director within the Company's organizational structure. The division is led by the Head of Internal Audit Division, who is appointed and dismissed by the President Director with approval from the Board of Commissioners. The Head of Internal Audit is authorized to communicate directly with the Board of Commissioners and its committees to inform any audit-related matters. However, such disclosure of information must be reported to the President Director.
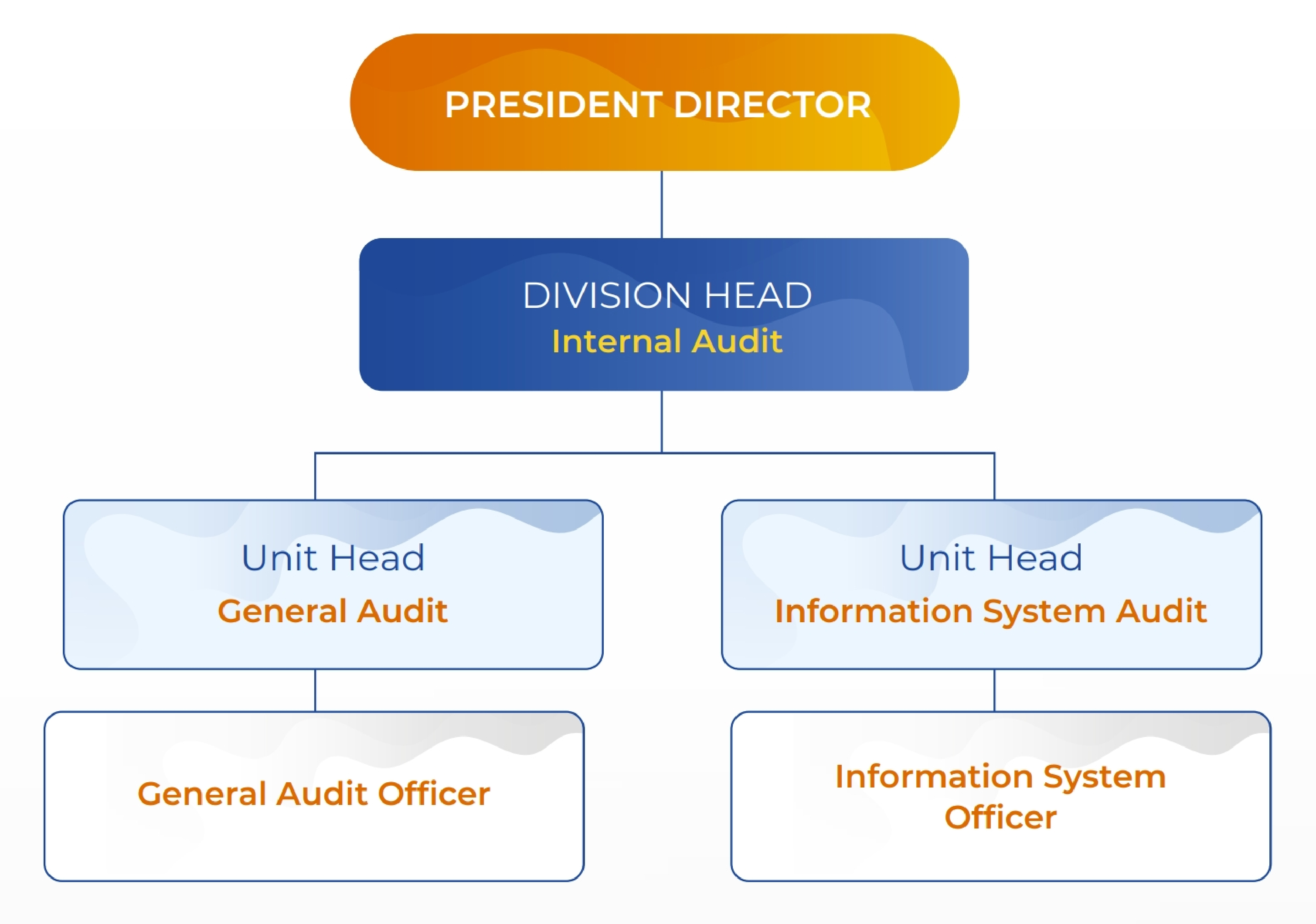
Duties and Responsibilities of Internal Audit Division
Based on the Internal Audit Charter, the Internal Audit Division is tasked with the following duties and responsibilities:
- Preparing and implementing the annual Internal Audit plan;
- Testing and evaluating the implementation of internal control and risk management systems in accordance with Company policy;
- Examining and assessing the efficiency and effectiveness in the areas of business, operations, finance, accounting, human capital, information technology, and other activities;
- Providing suggestions for improvement and objective information about the activities examined at all levels of management;
- Preparing an audit report and submitting the report to the President Director and the Board of Commissioners;
- Monitoring, analyzing, and reporting on the implementation of recommended improvements;
- Communicating with the Audit Committee in conducting supervision;
- Developing programs to evaluate the quality of internal audit activities being performed;
- Conducting special examinations if necessary.
Internal Audit Charter
The Internal Audit Division has a set of guidelines outlined in the Internal Audit Charter, ratified through the Board of Directors Decree No. KD-016/BRIDS/07/2023. This charter was designed to provide guidance to the Internal Audit Division in fulfilling its duties and responsibilities. The various aspects of the internal audit charter, including: Vision and Mission; Objectives of Internal Audit Activities; Structure and Position of the Internal Audit Division; Scope, Duties and Responsibilities of the Internal Audit Division; Authority of the Internal Audit Division; Professional Ethics; Internal Auditor Requirements; and Reporting.
Implementation of Internal Audit Duties
The Internal Audit Division conducted audits of work units according to the audit plan and assessed the implementation of improvement suggestions. In 2023, the Internal Audit Division regularly conducted audits on 10 subjects.
During its operations, the Internal Audit Division regularly coordinated through meetings with the Board of Directors, which occurred 4 times throughout 2023, and with the Audit Committee 4 times to address important findings and/or issues related to the Internal Audit Division responsibilities
Information on Directors & Employees with WPPE and WPEE Licenses
The number of members of the Board of Directors and employees who have licenses as Underwriter Representatives (WPEE) and/or Broker-Dealer Representatives (WPPE) as per June 2024 are presented in the following table:
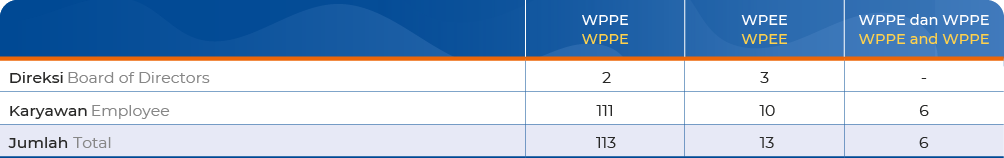
All members of the Board of Directors and employees holding WPEE and/or WPPE have obtained FSA Approval (OJK)



